What is a LEDES file? A 2021 guide to LEDES format for legal teams

LEDES is an acronym for Legal Electronic Data Exchange Standard, and LEDES format refers to legal invoices that adhere to those standards. Both legal operations teams and law firms can use LEDES files to streamline the billing process, save time, and gain better control over legal spend.
LEDES format has been around for more than two decades but has been updated several times, most recently in January 2020. Many legal teams have a preferred version, so we’ll cover the details of every type of LEDES file.
LEDES file definition
LEDES is a simple file format with specifications that support hourly billing, flat fee billing, expenses, multiple currencies, and tax. Created by the LEDES Oversight Committee (LOC) in 1995, this informal group of corporate legal departments, law firms, universities, and software vendors sought to address legal e-Billing software issues with a “standard format for the electronic exchange of billing and other information between corporations and law firms.”
LOC and their guidelines for LEDES format are guided by five basic principles:
- Keep it simple
- Make it unambiguous
- Diverge from existing formats as little as absolutely necessary
- Ask only for information the law firm is typically able to provide from their financial system
- Meet the needs of corporations, law firms, and legal industry software vendors to the maximum extent possible consistent with the first four criteria
The benefits of LEDES format for in-house counsel & legal operations
Ease of use for your law firms
With its efficient coding system, LEDES format reduces the time law firms spend on invoice creation and task descriptions while allowing your legal department to accept invoices in a uniform format for ease of processing.
Improved legal spend analysis for your legal department
Submitting invoices in LEDES format to an e-Billing solution allows legal teams to extract valuable invoice data for a better understanding of where and how their money is spent, and empowers them to control costs by viewing services in proper context. This level of insight can then be used in reporting and analysis to improve overall legal department operations, decision making, and spend management.
How LEDES files work
Instead of lumping costs into general areas, LEDES files drill down into the specifics. While a standard PDF invoice might break costs down into discovery, communication, and expenses, a LEDES file with task and activity codes would categorize costs even further.
For example, a LEDES invoice might include all of the following UTBMS codes:
- L310 Written Discovery
- L329 Document Production
- L330 Depositions
- A102 Research
- A106 Communicate (with client)
- A107 Communicate (with other outside counsel)
- E112 Court fees
- E113 Subpoena fees
- E120 Private investigators
- E115 Deposition transcripts
With this LEDES file, you have the ability to see exactly how and where money is spent. In this example, you might take a closer look at how much time was spent on research (A102) and the cost of a private investigator (E120). Were both expenses justified, or should you implement a cap on private investigator spend in the future?
Types of LEDES billing formats
Because LEDES files rely heavily on standardization, it’s important to specify which format your vendors should use. Remember, legal teams don’t necessarily use the most updated versions, so we’ll take you through each LEDES file from most basic to most detailed.
LEDES 1998
The original LEDES format, LEDES 1998, was created in 1998 but was quickly replaced by LEDES 1998B and 1998BI. LEDES 1998B is a pipe delimited format that contains 24 data fields. Currently, it is the most commonly used format in the U.S. due to its simplicity.
LEDES 1998BI is based on the 1998B format but is designed to accommodate legal bills created outside of the United States. Building off the original 24 data fields, the 1998BI version includes 51 total data fields that cover more detailed information such as law firm and client addresses, currency used, and data by timekeeper.
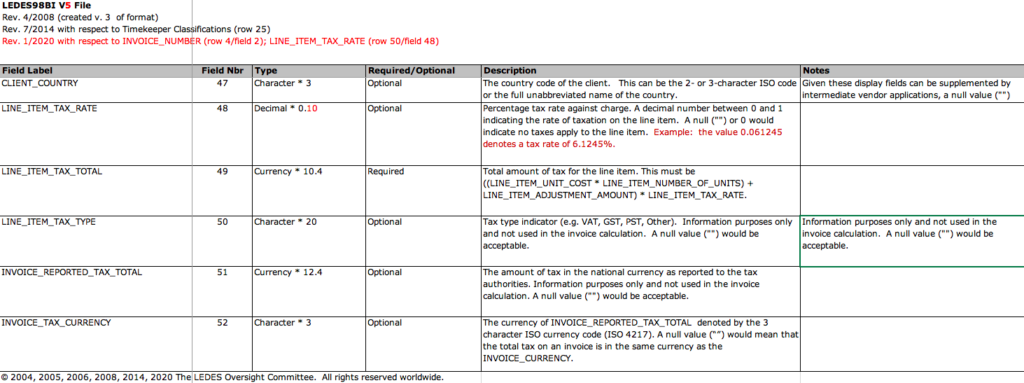
LEDES 1998B and LEDES 1998BI are the most basic LEDES formats with 51 data fields. Source
LEDES XML 2000
This XML file format was created in 2000 and includes 125 fields within seven segments:
- Firm
- Client
- Invoice
- Matter
- Timekeeper sum
- Fee
- Expense
LOC occasionally releases minor revisions to address typos or clarifications, but only major changes result in updated LEDES file version names.
LEDES XML 2000 has been officially ratified three times: in 2006, 2008, and most recently in January 2020. Those updates are referred to as LEDES XML 2.0, LEDES XML 2.1, and LEDES XML 2.2, respectively.
LEDES XML 2.0
The 2006 update took the total number of fields up to 153 and added eight more segments:
-
- Tax
- Tax summary
- Matter discount credit
- Tax matter discount credit
- Fee item discount credit
- Tax item fee
- Expense item discount credit
- Tax item expense
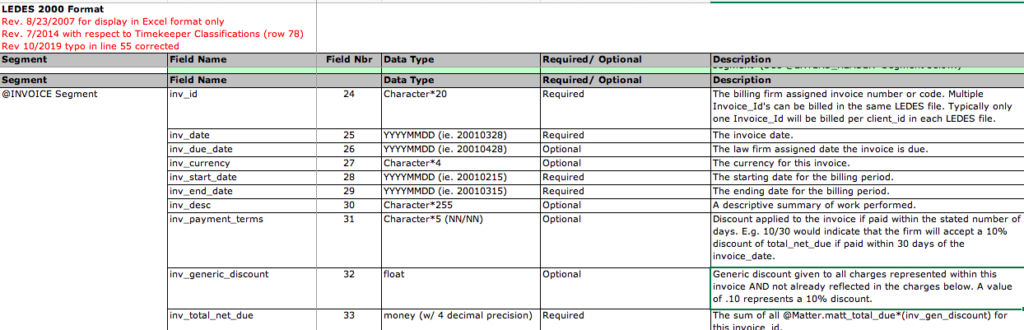
LEDES XML 2.0 format includes 153 data fields and a total of 15 segments. Source
The main goal of the 2006 ratification was to better address the complexity of itemizing taxes.
LEDES XML 2.1
In 2008, LOC released LEDES XML 2.1 to accommodate the increasing popularity of alternative fee arrangements (AFAs) and the move away from traditional hourly billing. The LEDES format documentation was revised again in August 2014 to clarify timekeeper classifications, but the file is still referred to as version 2.1.
LEDES XML 2.1 includes 191 data fields and added one new segment: Regulatory Statement.
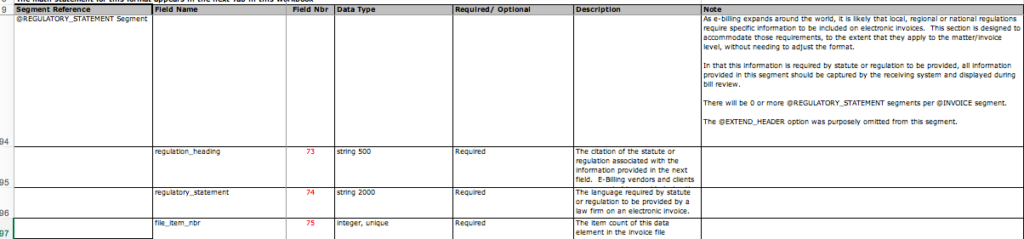
LEDES XML 2.1 includes a new segment, Regulatory Compliance. Source
LEDES XML 2.2
In 2020, LOC updated the LEDES format once again to include segments for Tiered Taxes, bringing the XML 2.2 LEDES format up to 205 data elements and 18 segments.
- Firm
- Tax
- Client
- Invoice
- Tax tier summary
- Tax tier detail
- Regulatory statement
- Matter
- Tax summary
- Matter discount credit
- Tax matter discount credit
- Timekeeper sum
- Fee
- Fee item discount credit
- Tax item fee
- Expense
- Expense item discount credit
- Tax item expense
Does your e-Billing solution support LEDES?
Whether you are thinking about adopting legal e-Billing software, or considering an alternative to your current e-Billing system, look for a solution like SimpleLegal that accepts the most commonly used LEDES file formats. Law firms based in the US typically use “LEDES 1998B” (which cannot be used for invoices with VAT-style tax or any non-USD invoice), while law firms outside the US typically use “LEDES 1998BI”.
If you’re concerned that some of the small, boutique law firms that you work with will not be able to use LEDES invoicing format, verify that your e-billing solution can process other formats as well. For example, SimpleLegal accepts invoices as PDFs as well as all types of LEDES invoices, so you and your law firms have several options.
For more information on modern e-Billing software and how to find a solution that is a good fit for both your legal department and your law firms, download our guide, 8 Ways to Vet Your e-Billing Solution for Law Firm Adoption.
This article has been updated to reflect new information and industry trends from the original article, published on April 2, 2020.


